Photo illustration: Twitter vs Facebook echo chamber
Twitter's algorithm-driven timeline amplifies polarized content, creating a more intense echo chamber compared to Facebook's friend-based network which fosters smaller, ideologically aligned groups. Explore the nuanced differences in echo chamber dynamics and their social impact in this article.
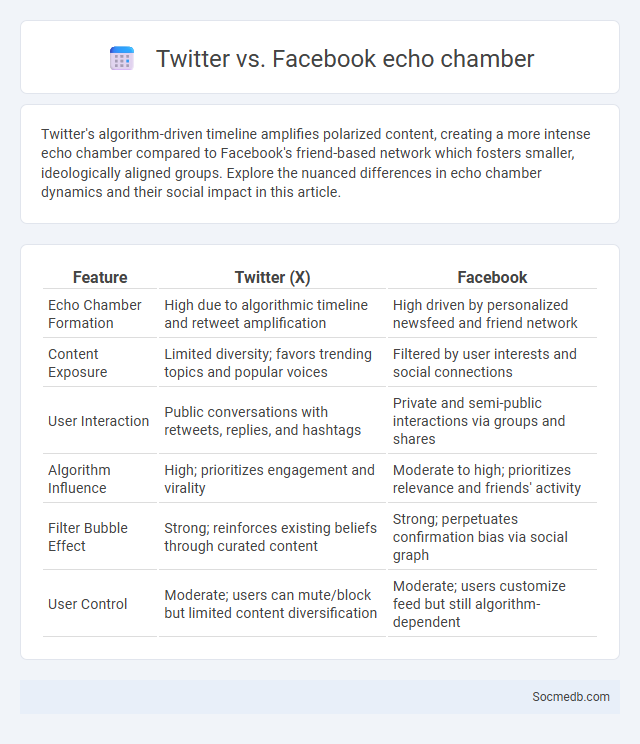
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Twitter (X) | |
|---|---|---|
| Echo Chamber Formation | High due to algorithmic timeline and retweet amplification | High driven by personalized newsfeed and friend network |
| Content Exposure | Limited diversity; favors trending topics and popular voices | Filtered by user interests and social connections |
| User Interaction | Public conversations with retweets, replies, and hashtags | Private and semi-public interactions via groups and shares |
| Algorithm Influence | High; prioritizes engagement and virality | Moderate to high; prioritizes relevance and friends' activity |
| Filter Bubble Effect | Strong; reinforces existing beliefs through curated content | Strong; perpetuates confirmation bias via social graph |
| User Control | Moderate; users can mute/block but limited content diversification | Moderate; users customize feed but still algorithm-dependent |
Understanding Echo Chambers: Definitions and Dynamics
Echo chambers in social media refer to environments where users are exposed predominantly to information and opinions that reinforce their existing beliefs, limiting exposure to diverse viewpoints. These dynamics arise from algorithmic personalization, user behavior, and homophily, which collectively amplify confirmation bias and polarize discourse. Analyzing interaction patterns and content flows within echo chambers is crucial for addressing misinformation and fostering critical thinking online.
Twitter's Echo Chamber: How Algorithms Shape Discourse
Twitter's Echo Chamber effect is driven by algorithms that prioritize content reinforcing users' existing beliefs, intensifying polarization and limiting exposure to diverse viewpoints. Machine learning models analyze engagement patterns to curate feeds, creating feedback loops that amplify homogeneous opinions. This phenomenon impacts political discourse and social interactions by reducing information diversity and fostering ideological segregation.
Facebook's Echo Chamber: Personalization and Information Bubbles
Facebook's echo chamber effect intensifies as its algorithm prioritizes personalized content that aligns with users' existing beliefs, creating information bubbles that limit exposure to diverse perspectives. This personalization reinforces confirmation bias by continuously curating news feeds and interactions within homogenous social networks. The consequence is a fragmented public discourse, where users are insulated from conflicting viewpoints, impacting democratic engagement and social cohesion.
Key Differences: Twitter Echo Chamber vs Facebook Echo Chamber
Twitter's echo chamber often amplifies rapid news and real-time opinions, creating tightly-knit communities driven by hashtags and trending topics. Facebook's echo chamber is shaped by personalized algorithms that prioritize content from friends and interest-based groups, resulting in slower but deep reinforcement of beliefs. Your experience on Twitter tends to be more immediate and fragmented, while Facebook's environment fosters prolonged engagement with like-minded perspectives.
Mechanisms of Echo Chamber Formation on Social Media
Echo chambers on social media form through algorithmic filtering that prioritizes content aligned with Your existing beliefs, reinforcing homogenous viewpoints. Social networks encourage selective exposure by connecting users with like-minded individuals, amplifying shared opinions and minimizing dissenting perspectives. This combination of personalized feeds and social interactions cultivates environments where diverse information is rarely encountered.
Psychological Impact of Echo Chambers on Users
Echo chambers on social media reinforce your preexisting beliefs by exposing you primarily to like-minded opinions, which can heighten cognitive biases and reduce critical thinking. This psychological impact often leads to increased polarization, anxiety, and a distorted perception of reality. Understanding this dynamic helps mitigate the negative effects on mental health and encourages more balanced information consumption.
Echo Chamber vs Filter Bubble: What’s the Difference?
Echo chambers and filter bubbles both limit your exposure to diverse opinions on social media but differ in mechanics; echo chambers occur when like-minded users reinforce similar views, while filter bubbles result from algorithms personalizing content based on your previous interactions. Understanding this distinction helps you recognize how platforms curate your feed, often narrowing your worldview and influencing your online behavior. Being aware of echo chambers and filter bubbles empowers you to seek varied perspectives and make more informed decisions.
Breaking Free: Strategies to Avoid Echo Chambers
Echo chambers on social media limit your exposure to diverse perspectives, reinforcing existing beliefs and potentially skewing your worldview. Engaging with a variety of sources, following accounts with differing opinions, and actively seeking out reputable news outlets can help break the cycle. Using tools like content filters and regularly reviewing your network can increase the breadth of your social media experience and enhance critical thinking.
The Role of Influencers in Sustaining Social Media Echo Chambers
Influencers play a critical role in sustaining social media echo chambers by consistently sharing content that aligns with your existing beliefs and preferences, thereby reinforcing your worldview. Their curated posts and endorsements create filtered information bubbles that limit exposure to diverse perspectives. This targeted reinforcement shapes user engagement and deepens ideological divides across social platforms.
The Future of Online Discourse: Mitigating Echo Chamber Effects
The future of online discourse will require advanced algorithms that diversify your social media feeds to mitigate echo chamber effects, fostering exposure to varied perspectives and reducing polarization. Implementing AI-driven content curation enhances critical thinking by presenting balanced viewpoints, while promoting digital literacy empowers users to recognize biases and seek credible sources. These strategies collectively create an online environment conducive to constructive dialogue and informed decision-making.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com