Photo illustration: Twitter vs Mastodon echo chamber
Twitter's algorithm-driven timeline intensifies echo chambers by amplifying similar viewpoints and polarizing users, while Mastodon's decentralized, community-moderated approach fosters diverse discussions and limits systemic bias. Explore this article to understand how platform design shapes social discourse and user experience.
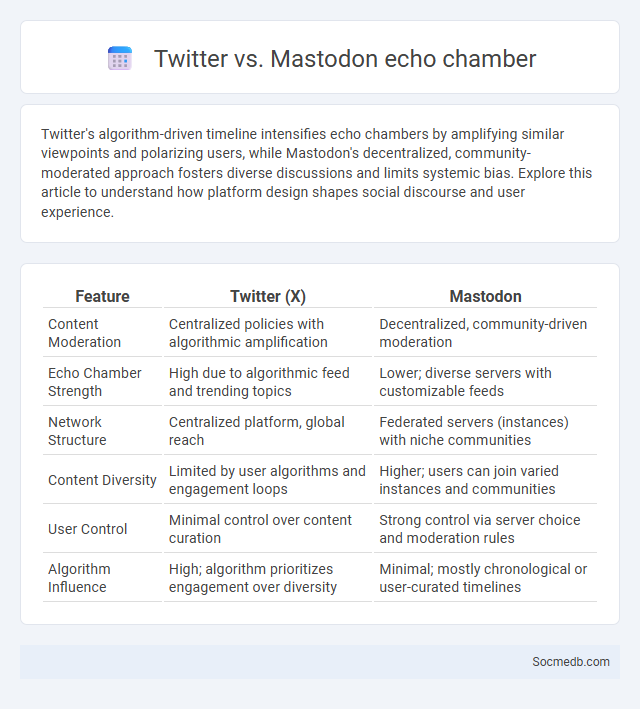
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Twitter (X) | Mastodon |
|---|---|---|
| Content Moderation | Centralized policies with algorithmic amplification | Decentralized, community-driven moderation |
| Echo Chamber Strength | High due to algorithmic feed and trending topics | Lower; diverse servers with customizable feeds |
| Network Structure | Centralized platform, global reach | Federated servers (instances) with niche communities |
| Content Diversity | Limited by user algorithms and engagement loops | Higher; users can join varied instances and communities |
| User Control | Minimal control over content curation | Strong control via server choice and moderation rules |
| Algorithm Influence | High; algorithm prioritizes engagement over diversity | Minimal; mostly chronological or user-curated timelines |
Introduction to Echo Chambers in Social Media
Echo chambers in social media occur when You engage primarily with content and opinions that reinforce Your existing beliefs, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. Platforms' algorithms amplify this effect by curating feeds based on Your interactions, creating insulated communities that can intensify polarization. Understanding echo chambers helps You recognize how information bubbles shape perceptions and influence online discourse.
Understanding Twitter's Algorithmic Echo Chambers
Twitter's algorithmic echo chambers shape your social media experience by prioritizing content that aligns with your previous interactions, reinforcing pre-existing beliefs. This filtering process limits exposure to diverse perspectives, intensifying ideological polarization and reducing conversational diversity. Recognizing the mechanics behind Twitter's recommendation system can help you actively seek balanced viewpoints and mitigate the effects of echo chambers.
Mastodon’s Decentralization: A Solution to Echo Chambers?
Mastodon's decentralized network structure distributes control across multiple independent servers, reducing the risk of algorithm-driven echo chambers commonly seen on centralized platforms like Facebook or Twitter. By allowing you to choose from various communities with distinct moderation policies, Mastodon promotes diverse viewpoints and authentic interactions. This decentralization empowers users to curate their social media experience, fostering a healthier online environment less prone to polarization.
Comparing User Experience: Twitter vs Mastodon
Twitter offers a streamlined user experience with a centralized platform and concise character limits, fostering fast-paced interactions and broad reach through trending hashtags. Mastodon provides a decentralized, federated network with customizable instances, emphasizing community moderation and user control for a more personalized and less commercialized environment. While Twitter excels in immediacy and widespread visibility, Mastodon's customizable timeline and privacy features appeal to users seeking a tailored and less algorithm-driven social media experience.
Community Moderation and Content Curation
Community moderation on social media ensures a safe and respectful environment by removing harmful content and enforcing platform guidelines, fostering positive interactions among users. Effective content curation highlights relevant and high-quality posts, enhancing user engagement and delivering a personalized experience tailored to Your interests. Combining these strategies supports vibrant online communities and maintains the integrity of social media ecosystems.
Virality, Trends, and Reinforcement Loops
Social media thrives on virality, where content rapidly spreads through shares and engagement, amplifying your reach exponentially. Trends emerge as users collectively interact with popular topics, creating a dynamic environment that keeps audiences engaged and constantly evolving. Reinforcement loops strengthen this cycle by rewarding user participation with increased visibility and social validation, driving continuous content sharing and interaction.
Filter Bubbles: Depth and Breadth of Perspectives
Filter bubbles limit your exposure to diverse viewpoints by showing content tailored to your existing beliefs and interests. This narrowing effect reduces the breadth of perspectives, reinforcing biases and hindering critical thinking. Understanding how algorithms curate your social media feed can help you break free from echo chambers and gain a deeper, more balanced understanding of issues.
Impact on Public Discourse and Polarization
Social media platforms have transformed public discourse by enabling rapid information sharing and amplifying diverse viewpoints, but they also contribute to echo chambers and ideological segregation. Algorithms prioritize engaging content, often favoring sensationalism and emotionally charged posts, which intensifies polarization and reduces exposure to opposing perspectives. This shift has reshaped political dialogue, hindering consensus-building and fostering increased social division.
Strategies to Break Echo Chambers on Both Platforms
Effective strategies to break echo chambers on social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter involve diversifying your content sources and actively engaging with differing viewpoints through comments and discussions. Algorithms are designed to show similar content, so intentionally following a variety of accounts and joining groups with contrasting opinions can broaden your perspective. Your proactive efforts to seek out credible information and challenge your own biases help create a more balanced and informed social media experience.
Future of Social Networking: Towards Diversity or Isolation?
Emerging trends in social media reveal a dual trajectory where platforms either foster diverse, global communities through advanced AI-driven content personalization or risk increasing user isolation by creating echo chambers that reinforce existing beliefs. Innovations in virtual reality and augmented reality aim to enhance social interaction, yet algorithms prioritizing engagement often contribute to fragmented networks. Understanding the balance between inclusivity and isolation is crucial for shaping the future landscape of social networking.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com