Photo illustration: WhatsApp vs Facebook Messenger spam
WhatsApp experiences lower spam rates compared to Facebook Messenger due to its end-to-end encryption and stricter user verification processes. Discover detailed spam prevention strategies and comparative analysis in this article.
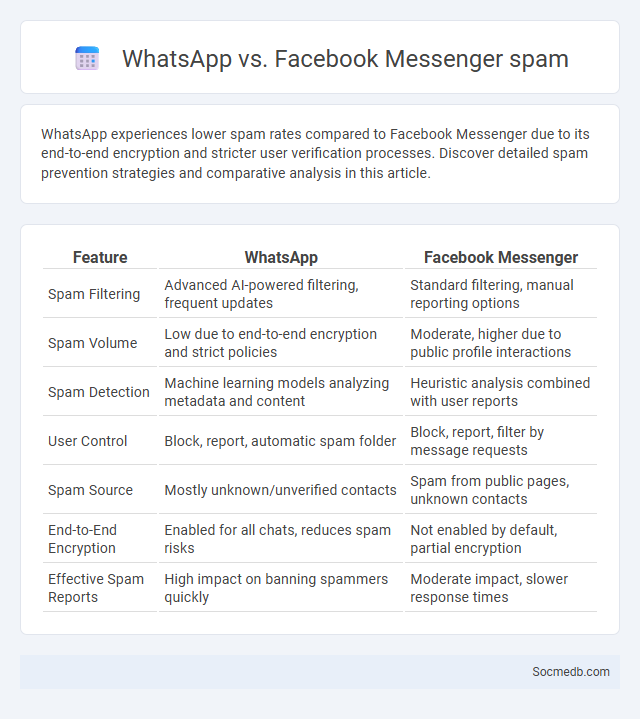
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Facebook Messenger | |
|---|---|---|
| Spam Filtering | Advanced AI-powered filtering, frequent updates | Standard filtering, manual reporting options |
| Spam Volume | Low due to end-to-end encryption and strict policies | Moderate, higher due to public profile interactions |
| Spam Detection | Machine learning models analyzing metadata and content | Heuristic analysis combined with user reports |
| User Control | Block, report, automatic spam folder | Block, report, filter by message requests |
| Spam Source | Mostly unknown/unverified contacts | Spam from public pages, unknown contacts |
| End-to-End Encryption | Enabled for all chats, reduces spam risks | Not enabled by default, partial encryption |
| Effective Spam Reports | High impact on banning spammers quickly | Moderate impact, slower response times |
Introduction to WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger
WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger are leading social media platforms designed for instant messaging, voice, and video calls worldwide. WhatsApp offers end-to-end encryption ensuring your conversations remain private and secure, while Facebook Messenger integrates seamlessly with Facebook, providing features like chatbots, group chats, and business communication tools. Both platforms support multimedia sharing and real-time communication, enhancing your social connectivity and engagement.
Defining Spam in Messaging Platforms
Spam in messaging platforms refers to unsolicited, irrelevant, or excessive messages sent to users, often with the intent of advertising, phishing, or spreading malware. Common examples include bulk promotional messages, deceptive links, and repetitive content that disrupts user experience and violates platform policies. Advanced spam detection employs machine learning algorithms analyzing message patterns, sender behavior, and user reports to maintain platform integrity and safeguard user privacy.
Common Types of Spam on WhatsApp
WhatsApp commonly faces spam in the form of unsolicited bulk messages, phishing links, and fake promotions designed to deceive users. Spam also includes chain messages that often spread misinformation or hoaxes, impacting user trust and platform integrity. Many users report encountering account takeover attempts through malicious links disguised as official WhatsApp communications.
Typical Spam Tactics on Facebook Messenger
Typical spam tactics on Facebook Messenger include sending unsolicited messages containing malicious links, phishing attempts, or fake promotions designed to steal personal information. Spammers often impersonate trusted contacts or reputable brands to trick users into clicking harmful links or providing sensitive data. These tactics exploit Messenger's instant communication features, increasing the risk of account compromise and spreading malware rapidly.
Spam Detection Features: WhatsApp vs Facebook Messenger
WhatsApp employs advanced spam detection features including automatic filtering of suspicious links and messages, leveraging machine learning algorithms to identify and block spam before it reaches Your inbox. Facebook Messenger incorporates robust spam detection by analyzing user reports and behavior patterns, using AI to flag and restrict spam accounts actively. Both platforms prioritize user safety but WhatsApp's end-to-end encryption enhances privacy while Facebook Messenger offers broader integration with social media for comprehensive spam control.
User Privacy and Security Measures
User privacy and security measures on social media platforms are crucial for protecting personal data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Features like end-to-end encryption, two-factor authentication, and customizable privacy settings empower you to control who can view your information and interactions. Regular updates and strict compliance with data protection regulations ensure that social media companies prioritize safeguarding user identities and online activities.
Reporting and Blocking Spam Messages
Social media platforms provide advanced tools for reporting and blocking spam messages to protect your account from unwanted content and potential scams. By utilizing built-in features such as report buttons, spam filters, and block options, you ensure a safer online experience and maintain the integrity of your social interactions. Regularly managing these settings helps prevent the spread of malicious content and preserves your digital privacy.
Effectiveness of Anti-Spam Algorithms
Anti-spam algorithms play a crucial role in maintaining the quality of your social media experience by effectively filtering out unwanted and harmful messages. These algorithms leverage machine learning techniques and real-time data analysis to identify and block spam with high accuracy, improving user engagement and platform security. Continuous updates and user feedback further enhance their performance, ensuring your interactions remain relevant and safe.
Comparing User Experiences with Spam
Social media platforms vary significantly in user experiences, especially regarding the prevalence of spam, which can disrupt your engagement and content sharing. Platforms like Instagram and Twitter utilize advanced algorithms and reporting tools to minimize spam, improving the quality of interactions. In contrast, more open networks such as Facebook Groups often face higher spam challenges, affecting user satisfaction and trust.
Future Trends in Messaging App Spam Prevention
Future trends in messaging app spam prevention emphasize advanced AI algorithms and machine learning models to detect and block spam in real time. Enhanced user authentication methods, including biometric verification and behavioral analysis, reduce the risk of automated spam bots. Integration of end-to-end encryption with spam filtering ensures both privacy and security without compromising message integrity.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com