Photo illustration: Deepfake vs Filters
Deepfake technology creates hyper-realistic manipulated videos that can deceive viewers, while social media filters typically enhance or alter appearances in real-time selfies without full fabrication. Discover the key differences and implications of deepfakes versus filters in this article.
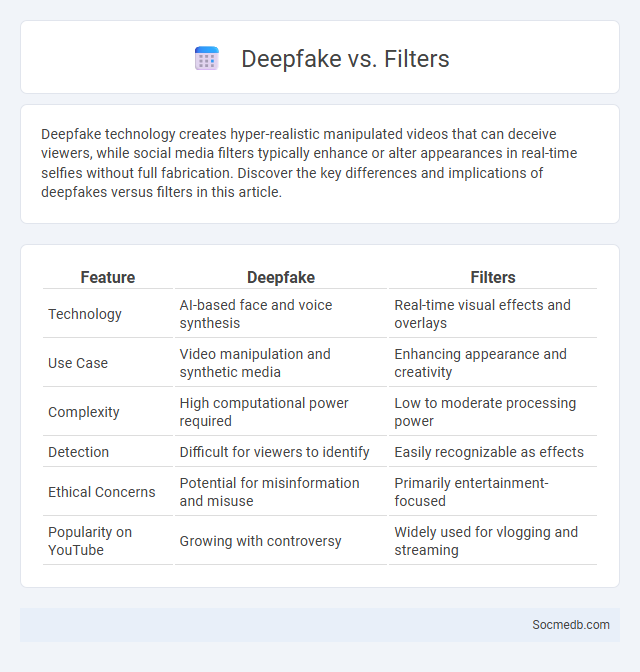
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Deepfake | Filters |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | AI-based face and voice synthesis | Real-time visual effects and overlays |
| Use Case | Video manipulation and synthetic media | Enhancing appearance and creativity |
| Complexity | High computational power required | Low to moderate processing power |
| Detection | Difficult for viewers to identify | Easily recognizable as effects |
| Ethical Concerns | Potential for misinformation and misuse | Primarily entertainment-focused |
| Popularity on YouTube | Growing with controversy | Widely used for vlogging and streaming |
Understanding Deepfakes: Definition and Technology
Deepfakes are synthetic media generated using advanced artificial intelligence algorithms, particularly deep learning techniques such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), to create realistic but fabricated videos or images of people. This technology manipulates facial expressions, voice, and movements, making it challenging to distinguish real content from fake, posing significant risks for misinformation and identity fraud. Understanding deepfakes can help you critically evaluate social media content and protect your digital interactions from deceptive manipulations.
What Are Filters? A Quick Overview
Filters are digital tools applied to photos or videos on social media platforms to enhance or alter their appearance by adjusting colors, brightness, contrast, and adding effects. These features help you create a specific mood or aesthetic, making your content more engaging and visually appealing to your audience. Popular apps like Instagram and Snapchat offer a variety of filters that are easy to use and instantly transform your posts.
Key Differences Between Deepfakes and Filters
Deepfakes use advanced AI algorithms to create hyper-realistic, manipulated videos or images that replace someone's likeness, posing significant risks to privacy and misinformation. Filters, on the other hand, apply real-time effects or enhancements to your photos and videos without altering the fundamental identity or content. Understanding these differences is crucial for protecting your digital presence and recognizing authentic versus manipulated media on social platforms.
How Deepfakes Are Created: AI and Machine Learning
Deepfakes are generated using advanced AI techniques such as deep learning and neural networks that analyze vast datasets of images and videos to create hyper-realistic synthetic media. Machine learning algorithms, particularly Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), play a critical role by pitting two networks against each other to produce increasingly convincing fake visuals. These technologies enable the seamless swapping of faces and manipulation of audio-visual content, raising significant concerns about authenticity and misinformation on social media platforms.
The Rise of Filters in Social Media
The rise of filters in social media has transformed the way users interact with digital content, enhancing visual appeal and personal expression. Platforms like Instagram, Snapchat, and TikTok employ advanced AI-driven filters to alter facial features, adjust lighting, and add creative effects, driving higher engagement and user retention. Your online presence can be amplified significantly by leveraging popular filters that resonate with current trends and audience preferences.
Deepfake Use Cases: Entertainment to Misinformation
Deepfake technology has revolutionized social media by enabling hyper-realistic video edits that enhance entertainment through realistic visual effects and celebrity impersonations. However, this powerful tool also poses significant risks as it facilitates the spread of misinformation by creating deceptive content that can manipulate public opinion and deceive viewers. Protecting Your online experience requires vigilance and awareness of how deepfakes are used to blur the line between reality and fiction.
Filters: Enhancing Visuals or Distorting Reality?
Filters on social media platforms enhance visuals by improving color, lighting, and overall aesthetic appeal, often increasing user engagement and content shareability. However, excessive use of filters can distort reality, promoting unrealistic beauty standards and contributing to issues like body dysmorphia and self-esteem problems. The balance between creative expression and authenticity remains a critical debate in the impact of social media filters.
Ethical Implications of Deepfakes vs Filters
Deepfakes pose significant ethical challenges by enabling realistic but fabricated videos that can spread misinformation, manipulate public opinion, and infringe on privacy rights. In contrast, filters primarily alter appearance in photos and videos for aesthetic purposes, raising concerns about self-image and authenticity rather than deception. Both technologies demand rigorous ethical guidelines to prevent misuse while balancing creative freedom and user protection on social media platforms.
Spotting Deepfakes and Filtered Content: Tips and Tools
Spotting deepfakes and filtered content on social media requires keen attention to inconsistencies in facial expressions, unnatural lighting, and glitches in video frames. Employing AI-powered tools like Deepware Scanner and Sensity can help verify the authenticity of suspicious media efficiently. Strengthen your digital literacy by cross-referencing content with trusted sources to protect Your online interactions from manipulated media.
The Future of Digital Content: Deepfakes and Filters
The future of digital content is rapidly evolving with advancements in deepfake technology and sophisticated filters, transforming the way social media users create and consume media. Deepfakes leverage artificial intelligence to generate hyper-realistic videos, raising significant concerns about authenticity and misinformation while offering new avenues for entertainment and personalized content. Enhanced filters enable users to modify images and videos with unprecedented precision, driving increased engagement but also necessitating stronger ethical guidelines and digital literacy education.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com