Photo illustration: Deepfake vs Shallowfake
Deepfake technology uses advanced AI to create hyper-realistic but entirely fabricated videos, while shallowfake manipulates existing media through simpler editing techniques like speeding up or slowing down footage. Explore this article to understand the implications and detection methods of deepfake and shallowfake content.
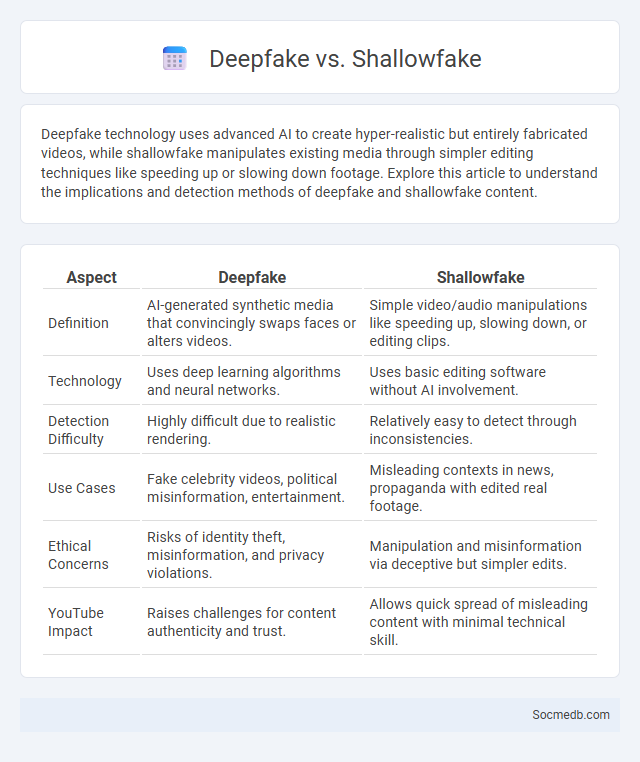
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Deepfake | Shallowfake |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | AI-generated synthetic media that convincingly swaps faces or alters videos. | Simple video/audio manipulations like speeding up, slowing down, or editing clips. |
| Technology | Uses deep learning algorithms and neural networks. | Uses basic editing software without AI involvement. |
| Detection Difficulty | Highly difficult due to realistic rendering. | Relatively easy to detect through inconsistencies. |
| Use Cases | Fake celebrity videos, political misinformation, entertainment. | Misleading contexts in news, propaganda with edited real footage. |
| Ethical Concerns | Risks of identity theft, misinformation, and privacy violations. | Manipulation and misinformation via deceptive but simpler edits. |
| YouTube Impact | Raises challenges for content authenticity and trust. | Allows quick spread of misleading content with minimal technical skill. |
Introduction to Media Manipulation: Deepfakes and Shallowfakes
Deepfakes and shallowfakes represent sophisticated forms of media manipulation that distort reality through AI-generated or edited videos and images. Deepfakes use advanced neural networks to create highly convincing fake content, while shallowfakes involve simpler editing techniques that still deceive viewers. Understanding these threats empowers you to critically evaluate social media content and safeguard your digital information.
What Is a Deepfake? Understanding AI-Generated Deception
Deepfakes are synthetic media created using artificial intelligence techniques such as deep learning and generative adversarial networks (GANs) to fabricate realistic images, videos, or audio of people saying or doing things they never did. This AI-generated deception poses significant risks in social media by enabling the spread of misinformation, identity fraud, and political manipulation. Understanding deepfake technology involves recognizing its ability to alter facial expressions, voice patterns, and contexts with high accuracy, making it challenging to detect without specialized tools.
Defining Shallowfake: Simple Editing, Serious Impact
Shallowfake refers to digitally altered social media content created using basic editing tools like cropping, speed manipulation, or color adjustments, rather than sophisticated AI-based deepfake technology. These minor modifications can significantly distort reality, misleading audiences and damaging reputations through deceptively altered videos or images. Platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and TikTok face challenges detecting and addressing shallowfakes due to their subtle, non-technical nature but profound impact on public perception.
Deepfake vs Shallowfake: Key Differences in Technology
Deepfake technology uses advanced artificial intelligence, such as deep learning algorithms and neural networks, to create highly realistic, synthetic video or audio content that can convincingly mimic real people. Shallowfake employs simpler editing techniques like speeding up, slowing down, or altering audio and video clips without generating entirely new content, making detection relatively easier compared to deepfakes. The sophistication and potential for deception in deepfakes pose significant challenges for authenticity verification and digital media trust on social media platforms.
Techniques Used: Deep Learning vs Basic Manipulation
Deep learning techniques in social media leverage neural networks to analyze vast data, enabling sophisticated content moderation, sentiment analysis, and personalized recommendations. Basic manipulation methods rely on simpler algorithms and manual adjustments to manage posts, detect spam, or boost engagement through keyword filtering and pattern recognition. The integration of deep learning enhances accuracy and scalability, significantly outperforming traditional manipulation approaches in handling complex social media dynamics.
Real-World Examples of Deepfakes and Shallowfakes
Deepfakes have been notably used in social media platforms like Twitter and Facebook where manipulated videos, such as a convincing deepfake of Barack Obama created by BuzzFeed and filmmaker Jordan Peele, highlighted the risks of misinformation. Shallowfakes, which involve simple video editing techniques like speeding up or repeating footage, surfaced prominently during the 2020 U.S. presidential election with altered clips of political speeches spreading rapidly across TikTok and Instagram. Both deepfakes and shallowfakes pose significant challenges to digital trust and content verification in the social media ecosystem.
Dangers and Ethical Concerns: Comparing Both Threats
Social media platforms pose significant dangers including data privacy breaches, cyberbullying, and misinformation spread, which can lead to real-world harm and societal polarization. Ethical concerns arise from algorithmic biases, exploitation of user data for targeted advertising, and lack of transparency in content moderation policies. Both threats require robust regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines to protect users and ensure responsible digital communication.
Detection Methods for Deepfakes and Shallowfakes
Detection methods for deepfakes and shallowfakes on social media leverage advanced machine learning algorithms, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), to identify visual and auditory inconsistencies. Techniques such as forensic analysis examine pixel-level anomalies, frame coherence, and audio-visual synchronization, while metadata verification cross-checks timestamps and source data to authenticate content. Emerging tools also utilize blockchain-based provenance tracking and user behavior analysis to enhance the reliability of fake media detection in real-time social media environments.
Legal and Social Implications of Media Fakery
Social media platforms face increasing challenges from media fakery, which involves the creation and dissemination of false or manipulated content that can mislead users and distort public perception. Legal frameworks are evolving to address issues such as defamation, intellectual property infringement, and the spread of disinformation, aiming to hold creators and distributors accountable while protecting freedom of expression. Your awareness of these legal and social implications is crucial for critically evaluating content and supporting media literacy initiatives to combat the harmful effects of fake media online.
The Future: Combating Deepfakes and Shallowfakes
Emerging technologies in social media utilize advanced AI detection tools and blockchain verification to combat the rise of deepfakes and shallowfakes, protecting content authenticity. Your online security depends increasingly on platforms implementing real-time video authentication and user education initiatives to identify manipulated media. Continuous innovation in forensic algorithms and cross-platform collaboration remains crucial to maintaining trust in digital communications.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com