Photo illustration: Fair Use vs Educational Use
Fair Use allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes like commentary or criticism, while Educational Use permits the use of content specifically for teaching and learning in non-commercial settings. Explore this article to understand the distinctions and legal boundaries between Fair Use and Educational Use on social media platforms.
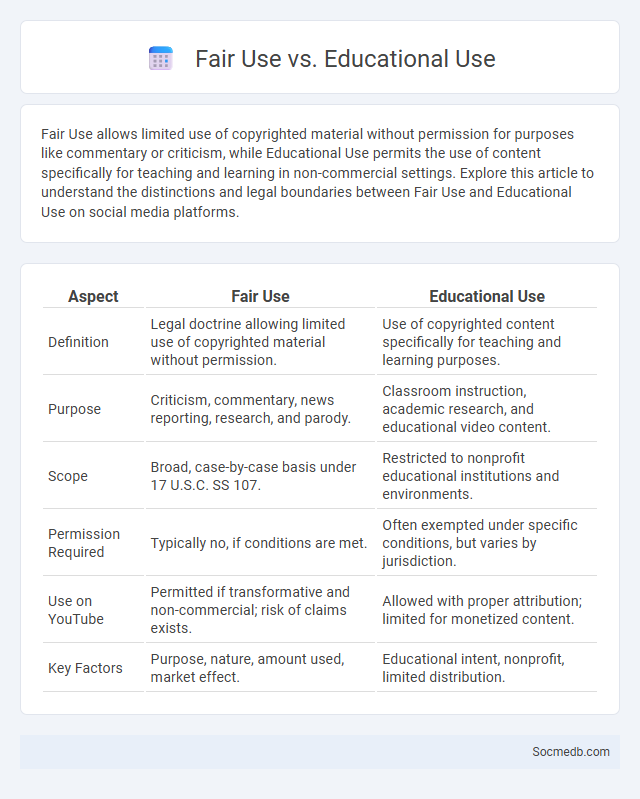
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Use | Educational Use |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal doctrine allowing limited use of copyrighted material without permission. | Use of copyrighted content specifically for teaching and learning purposes. |
| Purpose | Criticism, commentary, news reporting, research, and parody. | Classroom instruction, academic research, and educational video content. |
| Scope | Broad, case-by-case basis under 17 U.S.C. SS 107. | Restricted to nonprofit educational institutions and environments. |
| Permission Required | Typically no, if conditions are met. | Often exempted under specific conditions, but varies by jurisdiction. |
| Use on YouTube | Permitted if transformative and non-commercial; risk of claims exists. | Allowed with proper attribution; limited for monetized content. |
| Key Factors | Purpose, nature, amount used, market effect. | Educational intent, nonprofit, limited distribution. |
Understanding Fair Use: Legal Foundations and Principles
Fair use is a critical legal principle that permits limited use of copyrighted material on social media for purposes such as commentary, criticism, or education without infringing on the original creator's rights. Its foundation lies in balancing the creator's exclusive rights with the public's interest in free expression, governed by factors including the purpose of use, nature of the work, amount used, and market effect. Understanding these principles helps social media users navigate content sharing responsibly while minimizing legal risks.
Educational Use Explained: Exceptions and Limits
Social media platforms offer innovative educational tools that facilitate interactive learning and knowledge sharing, yet strict regulations govern data privacy and content accuracy to protect users. Exceptions to typical restrictions include the use of copyrighted materials under fair use provisions for educational purposes, enabling educators to freely share resources. However, limitations are enforced through platform policies and legal frameworks to prevent misinformation, cyberbullying, and unauthorized data exploitation in educational settings.
Fair Dealing vs. Fair Use vs. Educational Use: Key Differences
Fair Dealing, Fair Use, and Educational Use represent distinct legal frameworks governing the permissible use of copyrighted material on social media platforms. Fair Dealing, common in countries like the UK and Canada, restricts usage to specific purposes such as research or criticism, while Fair Use, primarily in the U.S., allows broader, case-by-case analysis including commentary, news reporting, and transformative uses. Educational Use typically permits copyrighted content for teaching or learning contexts but requires adherence to institutional policies and often overlaps with Fair Use or Fair Dealing depending on jurisdiction.
Core Criteria for Fair Use in Digital Content
Fair use in digital content hinges on four core criteria: the purpose and character of the use, the nature of the original work, the amount and substantiality of the portion used, and the effect on the market value of the original. Social media platforms often navigate these elements by promoting transformative uses such as commentary, criticism, or educational purposes while avoiding substantial replication of copyrighted content. Understanding these criteria is crucial for creators and users to legally share and remix digital media without infringing copyright laws.
Educational Exemptions: What Educators Need to Know
Educational exemptions in social media regulations protect platforms used by educators from certain legal liabilities, enabling safer sharing of academic content. Understanding Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act is crucial for educators to navigate content moderation and liability issues effectively. Schools and educators must stay informed about state-specific laws and platform policies to safeguard student privacy and comply with educational exemptions.
Common Misconceptions about Fair Use and Education
Many people mistakenly believe that any content used for educational purposes automatically qualifies as fair use, but this is not always the case under social media guidelines. Fair use depends on factors such as the purpose, nature, amount used, and effect on the market value of the original work, which you must carefully consider before sharing. Understanding these nuances can help you avoid copyright infringement while utilizing social media platforms for education.
Case Studies: Legal Precedents in Fair and Educational Use
Case studies on social media reveal landmark legal precedents in fair and educational use, highlighting how courts balance content creators' rights with public interest. Notable cases, such as Campbell v. Acuff-Rose Music, establish criteria for transformative use, shaping how your educational materials incorporate copyrighted media without infringement. Understanding these precedents ensures compliance while maximizing the legal use of social content in academic and training environments.
Navigating Copyright Pitfalls in Academic Settings
Navigating copyright pitfalls in academic settings requires a clear understanding of fair use policies and proper attribution of sources on social media platforms. You must ensure that any shared academic content complies with copyright laws to avoid legal issues and protect original creators' rights. Utilizing licensed materials and seeking permission when necessary fosters respect for intellectual property while enhancing your academic credibility online.
Best Practices for Responsible Content Usage
Ensure your social media posts respect privacy by obtaining consent before sharing personal information or images. Use accurate and verified information to prevent the spread of misinformation and maintain credibility. You should engage with content ethically by avoiding harmful or offensive material and promoting positive, inclusive interactions.
Future Trends: Adapting Fair Use in Modern Education
Future trends in social media emphasize adapting fair use policies to support modern education, ensuring that digital content is accessible while respecting copyright laws. As educators increasingly rely on platforms like YouTube and Instagram for teaching materials, understanding and applying fair use exemptions becomes essential for your institution's compliance and innovation. Advanced AI-driven content filtering and licensing models are expected to streamline permissions, allowing seamless integration of user-generated media in educational settings.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com