Photo illustration: Community Notes vs Third-party Fact-checkers
Community Notes leverages crowdsourced insights from diverse social media users to identify misinformation, while third-party fact-checkers rely on expert analysis and verification processes. Explore this article to understand the strengths and limitations of both approaches in combating online falsehoods.
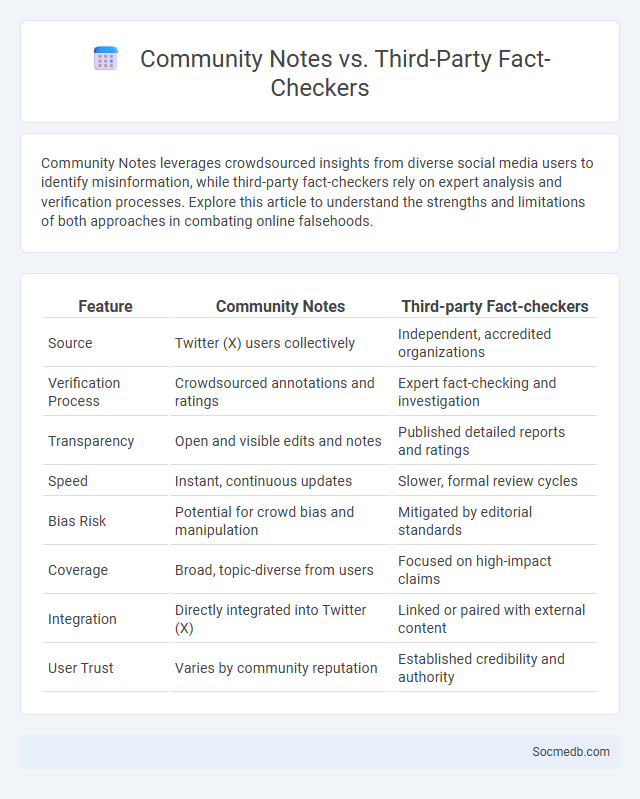
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Community Notes | Third-party Fact-checkers |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Twitter (X) users collectively | Independent, accredited organizations |
| Verification Process | Crowdsourced annotations and ratings | Expert fact-checking and investigation |
| Transparency | Open and visible edits and notes | Published detailed reports and ratings |
| Speed | Instant, continuous updates | Slower, formal review cycles |
| Bias Risk | Potential for crowd bias and manipulation | Mitigated by editorial standards |
| Coverage | Broad, topic-diverse from users | Focused on high-impact claims |
| Integration | Directly integrated into Twitter (X) | Linked or paired with external content |
| User Trust | Varies by community reputation | Established credibility and authority |
Introduction: Understanding Fact-Checking Ecosystems
Fact-checking ecosystems play a crucial role in maintaining the credibility of social media platforms by systematically verifying information shared across networks. These ecosystems involve a complex interaction between technology, independent fact-checkers, and user participation to identify and correct misinformation swiftly. By engaging with these resources, your ability to discern accurate information improves, reinforcing trust and promoting informed online communities.
What Are Community Notes?
Community Notes is a feature on social media platforms that allows users to collaboratively add context to tweets or posts by flagging misinformation and providing accurate information. You can contribute to creating a more trustworthy online environment by submitting notes that clarify misleading content, which are then reviewed and rated by the community. This transparent process helps improve the quality of information and fosters informed discussions across social networks.
How Third-party Fact-checkers Operate
Third-party fact-checkers collaborate with social media platforms by reviewing flagged content for accuracy using evidence-based research and verified sources. They apply standardized evaluation criteria to identify misinformation, often issuing corrections or labels to inform Your understanding. This process helps maintain platform integrity by reducing the spread of false information and promoting credible content.
Key Differences Between Community Notes and Third-party Fact-checkers
Community Notes rely on crowdsourced input from diverse users to identify misinformation, promoting transparency and collective verification, while Third-party Fact-checkers use specialized professionals and rigorous editorial standards to evaluate claims independently. You benefit from Community Notes' real-time updates and inclusive perspective, contrasting with the more authoritative, expert-driven assessments provided by Third-party Fact-checkers. Both systems complement each other by enhancing social media platforms' accuracy through different verification methods and scopes.
Strengths of Community Notes in Combating Misinformation
Community Notes harness the collective intelligence of diverse users to identify and address misinformation quickly and effectively. By allowing your contributions to add context and fact-check content in real-time, the platform enhances transparency and trust across social networks. This collaborative approach leverages crowdsourced insights to improve information accuracy and reduce the spread of false content.
Advantages and Limitations of Third-party Fact-checkers
Third-party fact-checkers on social media platforms enhance content credibility by reducing misinformation and promoting accurate information through independent verification processes. Their presence helps users identify false claims, fostering a more informed online community and improving public discourse quality. However, limitations include potential biases in fact-checking decisions, slower response times, and challenges in scaling efforts across vast volumes of content.
Transparency and Accountability: Community vs. Professional Approaches
Transparency and accountability on social media platforms differ significantly between community-driven and professional approaches. Community-based models emphasize open dialogue and crowd-sourced moderation, fostering trust through collective responsibility and user participation. Your engagement benefits from clear guidelines and consistent enforcement that professional teams provide, ensuring platform integrity and user safety.
Impact on Public Trust and Engagement
Social media platforms significantly influence public trust by shaping the flow of information, where misinformation can rapidly erode confidence in institutions and news sources. Your engagement on these platforms impacts the spread of authentic content, fostering transparency and community interaction. Effective management of social media tools enhances informed public discourse, reinforcing trust and civic participation.
Challenges Facing Both Systems
Social media platforms face significant challenges related to content moderation, misinformation, and user privacy across both centralized and decentralized systems. Centralized platforms struggle with controlling harmful content while maintaining free speech, whereas decentralized systems encounter difficulties in enforcing policies without centralized authority. Both models must address scalability and security issues to protect user data and ensure a safe online environment.
Future Perspectives: Towards a Collaborative Fact-Checking Model
Future perspectives on social media emphasize a collaborative fact-checking model that leverages AI algorithms and human expertise to combat misinformation effectively. Your participation in community-driven verification processes enhances the accuracy and credibility of content shared across platforms. This approach promotes transparency and trust by decentralizing fact-checking responsibilities among users, platforms, and third-party organizations.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com