Photo illustration: Fake News vs Hoaxes
Fake news involves deliberately fabricated information presented as legitimate news to mislead audiences, while hoaxes are false claims or stories designed to deceive for amusement or gain. Explore this article to understand the differences and impacts of fake news and hoaxes on social media.
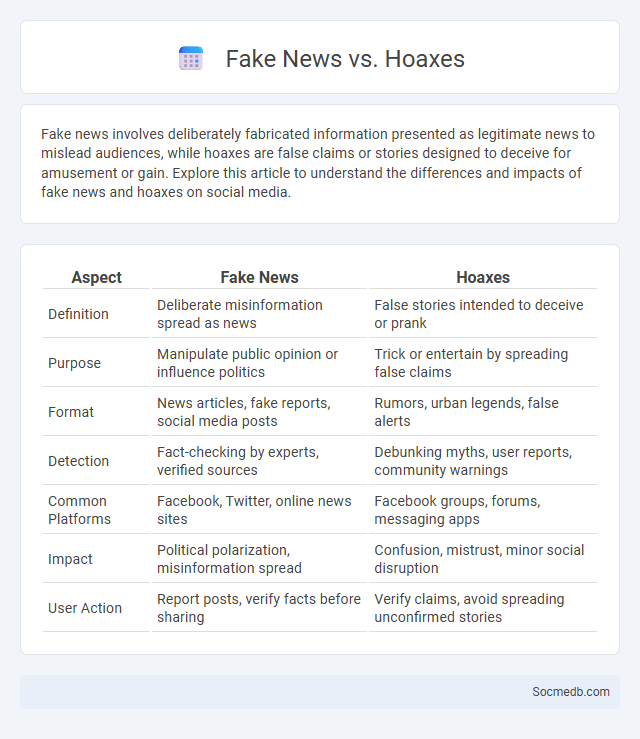
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fake News | Hoaxes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate misinformation spread as news | False stories intended to deceive or prank |
| Purpose | Manipulate public opinion or influence politics | Trick or entertain by spreading false claims |
| Format | News articles, fake reports, social media posts | Rumors, urban legends, false alerts |
| Detection | Fact-checking by experts, verified sources | Debunking myths, user reports, community warnings |
| Common Platforms | Facebook, Twitter, online news sites | Facebook groups, forums, messaging apps |
| Impact | Political polarization, misinformation spread | Confusion, mistrust, minor social disruption |
| User Action | Report posts, verify facts before sharing | Verify claims, avoid spreading unconfirmed stories |
Understanding Fake News: Definitions and Impact
Fake news refers to deliberately fabricated information intended to deceive readers, often spreading misinformation through social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. This phenomenon significantly impacts public opinion, undermining trust in legitimate news sources and fueling political polarization. Studies indicate that false news spreads faster and reaches more people than truthful content, making critical media literacy essential for users to discern credible information online.
What are Hoaxes? Key Characteristics
Hoaxes on social media are deliberately fabricated false information designed to deceive users and spread misinformation rapidly. Key characteristics include sensational or emotionally charged content, lack of credible sources, and often a call to share or take immediate action. These posts exploit trust and cognitive biases, making them viral and challenging to debunk.
Fake News vs. Hoaxes: Core Differences
Fake news consists of deliberately fabricated content designed to mislead and manipulate public opinion, often mimicking legitimate news sources. Hoaxes are deceptive schemes or pranks that may not always carry a political agenda but aim to trick or entertain at the expense of truth. Understanding these core differences empowers your ability to critically evaluate information and avoid spreading misinformation on social media platforms.
Historical Evolution of Misinformation
Misinformation on social media traces back to the early 2000s with the rise of platforms like MySpace and Facebook, enabling rapid content sharing without verification. The 2010s saw the explosive growth of Twitter and Instagram, amplifying the speed and reach of false information during events like the 2016 US presidential election. Recent advances in AI-generated deepfakes and bot networks further complicate identification and containment of misinformation across platforms.
Common Motivations Behind Spreading Fake News
Common motivations behind spreading fake news on social media include the desire for attention, financial gain through ad revenue or clickbait, and political or ideological influence. Individuals or groups exploit emotionally charged content to manipulate public opinion or sow discord, often targeting vulnerable or uninformed audiences. Understanding these drivers can help you critically evaluate the information you encounter and avoid contributing to misinformation.
Case Studies: Notorious Hoaxes and Fake News Incidents
Social media platforms have been central to several notorious hoaxes and fake news incidents, such as the 2016 U.S. presidential election interference and the COVID-19 misinformation campaigns. Case studies reveal how viral misinformation on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram manipulated public opinion and fueled societal divisions. These incidents highlight the urgent need for enhanced fact-checking algorithms and platform accountability to curb the spread of false information.
Detecting and Identifying Fake News
Detecting and identifying fake news on social media requires analyzing content authenticity through fact-checking algorithms and AI-powered tools that assess source credibility and consistency. Your ability to discern misinformation improves with awareness of common manipulation tactics, such as sensational headlines and doctored images. Leveraging reputable verification platforms and cross-referencing multiple sources enhances the accuracy of news consumed on digital networks.
Psychological Effects of Misinformation
Misinformation on social media platforms significantly impacts mental health by increasing anxiety, fear, and confusion among users. Exposure to false information triggers cognitive biases, leading to distorted perceptions of reality and reinforcing existing beliefs. These psychological effects undermine trust in credible sources and contribute to widespread social polarization.
Tools and Strategies to Combat Fake News and Hoaxes
Advanced fact-checking tools like Snopes, FactCheck.org, and AI-driven platforms are essential for verifying the authenticity of social media content. Strategies such as promoting digital literacy, implementing algorithmic filters, and encouraging user reporting help identify and reduce the spread of fake news and hoaxes. Collaborative efforts between social media companies, governments, and independent organizations enhance transparency and trust in online information ecosystems.
The Future of Truth: Building Media Literacy
The future of truth in social media hinges on cultivating advanced media literacy skills to discern credible information from misinformation and disinformation. Developing critical thinking and fact-checking abilities among users enhances their capacity to evaluate content authenticity, reducing the spread of fake news. Integrating comprehensive media education programs across digital platforms strengthens public resilience against manipulation and promotes informed decision-making in the digital age.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com